Tanning: What You Need to Know
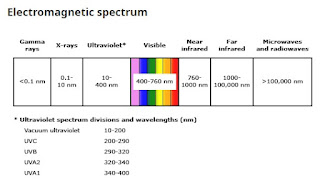
Suntan, the darkening of the skin following exposure to UV radiation, has cultural, cosmetic, and physiological significance. Despite the perception of a suntan as a healthy glow, the process itself is indicative of cellular damage. Ultraviolet Radiation and Skin: UV radiation, comprising UVA (320-400 nm), UVB (280-320 nm), and UVC (100-280 nm), is emitted by the sun. When UV rays reach the skin, they interact with chromophores such as melanin, DNA, and proteins, leading to a range of biological responses. Melanogenesis: Melanin, the pigment responsible for skin, hair, and eye color, plays a vital role in suntan. Upon exposure to UV radiation, melanocytes produce and distribute more melanin to neighboring keratinocytes. This increase in melanin pigment results in the darkening of the skin. Photochemical and Photobiological Effects: UV radiation induces numerous photochemical and photobiological effects on the skin, including DNA damage, oxidative stress, and inflammation. These proces...